Document #: HHS-OCIO-OES-2024-11-007
Version #: 3.0
Last Reviewed: 11/2024
Next Review: 11/2027
Owner: OCIO/OES
Approved By: Jennifer Wendel, HHS Chief Information Officer (CIO)
Table of Contents
- Nature of Changes
- Purpose
- Background
- Scope
- Authorities
- Policy
- Roles and Responsibilities
- 7.1. HHS Chief Information Officer (CIO)
- 7.2. HHS Chief Enterprise Architect (CEA)
- 7.3. HHS Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
- 7.4. HHS Senior Agency Official for Records Management (SAORM)
- 7.5. HHS IT Capital Planning and Investment Control (CPIC) Officer
- 7.6. HHS Enterprise Architecture Review Board (EARB)
- 7.7. HHS Vendor Management Office (VMO)
- 7.8. OpDiv CIO
- 7.9. OpDiv CEA
- 7.10. OpDiv CISO
- 7.11. OpDiv IT Capital Planning and Investment Control (CPIC) Officer
- 7.12. Business Owner
- 7.13. System Owner
- Information and Assistance
- Effective Date and Implementation
- Approval
Appendix D: Forms and Templates
1. Nature of Changes
This HHS Policy for Information Technology (IT) System Inventory Management (hereafter referred to as Policy) supersedes the current HHS Policy for IT System Inventory Management (HHS-OCIO-OES-2020-12-011).
Major revisions to this Policy include an updated list of authorities, new roles and responsibilities, updated procedures, standards, and guidance. This Policy incorporates the current federal policies and directives as specified by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB), the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (herein HHS or Department).
NOTE: Appendices are subject to change at any time. The official version of this Policy resides in the Enterprise IT Policy Library.
2. Purpose
The purpose of this Policy is to direct HHS entities (i.e., Operating Divisions [OpDivs] and Staff Divisions [StaffDivs]) to establish and maintain an enterprise-wide inventory of HHS IT systems by providing guidance and baseline standards for maintaining a comprehensive inventory of all IT systems and related information. This Policy also establishes the authoritative source for the HHS IT System Inventory (henceforth “the IT System Inventory”) and the stewards responsible for maintaining the availability and accuracy of the information.
3. Background
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) Circular A-130, Management of Federal Information Resources, directs all federal agencies to “develop an enterprise architecture (EA) that describes the baseline architecture, target architecture, and a transition plan to get to the target architecture.” As part of the duties to define and manage both current and target architecture, the responsibility for the maintenance of the IT System Inventory is under the purview of the HHS Enterprise Architecture (EA) Program.
Having visibility into the IT System Inventory across the Department facilitates managing information resources, IT planning, budgeting, acquisition, and reporting. Maintaining the IT System Inventory involves coordination and collaboration of all HHS OpDivs and StaffDivs. It is essential that all HHS entities keep an accurate, standardized, and current inventory of IT systems.
In the context of this Policy, an Information System is “a discrete set of information resources organized for the collection, processing, maintenance, transmission, and dissemination of information” (See NIST SP 800-59 under Information System from 44 U.S.C., Sec. 3502 (8)). This applies to all IT systems either owned or operated on behalf of and used to support HHS’s or OpDivs’ mission.
An IT system is the codification of business requirements, automated to support a specific mission- or business-related function IT typically encompasses hardware, software, information, data, applications, and communications.
As shown in Figure 2 (See Appendix C, Subsection 3), the relationship among key data stores for IT systems inventory management is as follows:
3.1. HHS EANow
EANow is the system that assigns the Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) for each IT system across HHS. As a result, EANow is the system of record for all IT systems across HHS.
3.2. HHS Security Data Warehouse (HSDW)
HSDW is “the Department’s authoritative source for all system security-related data and it is populated using submissions transmitted by each of the OpDivs on a [pre-defined] recurring cycle.1” This system is managed by HHS OCIO Office of Information Security (OIS).
3.3. Security Governance Risk and Compliance (SGRC) Archer
Commonly referred to across HHS as Archer, this “SGRC maintains information on the IT system, sub-system, major/minor, child or standalone system – against which security categories are assigned, controls are allocated and assessed, and privacy threshold assessment/privacy impact assessments are created.”2 This system is managed by HHS OCIO OIS.
The rollout of Archer across all HHS OpDivs is currently in progress. HSDW will continue to be used even after the Archer rollout is completed.
As this Policy is focused on IT systems, all software inventory considerations should be understood as a separate initiative from this IT Systems Inventory Policy. For more information regarding software inventory requirements, please reference the HHS Policy for IT Asset Management (ITAM).
4. Scope
This Policy applies to all HHS entities and organizations that use or maintain IT systems that conduct business for or are owned or operated on behalf of the Department. This Policy does not supersede any applicable law or Department policy or guidance unless specified in this document.
OpDivs/StaffDivs may create a more prescriptive policy specific to their requirements based on, but not less restrictive than, this Policy.
5. Authorities
The authorities for this Policy include:
Federal Laws
- Clinger-Cohen Act of 1996 (40 U.S.C. Chapter 111 Information Technology Management, General; 40 U.S.C. Chapter 113 Responsibility for Acquisitions of Information Technology)
- E-Government Act of 2002, Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002
- Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA) of 2014 (44 U.S.C. Chapter 35 Coordination of Federal Information Policy)
- Federal Information Technology Acquisition Reform Act (FITARA) of 2014
- FITARA Enhancement Act of 2017
- Making Electronic Government Accountable by Yielding Tangible Efficiencies (MEGABYTE) Act of 2016
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication (SP) 800-57 Part 1, Revision 5
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication (SP) 800-59 under Information System from 44 U.S.C., Sec. 3502 (8)
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication (SP) 800-37 Revision 2
- Senior Agency Official for Records Management (SAORM) 2023 Annual Report
- National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) Bulletin 2010-02
OMB Circulars
- OMB Circular A-11, Preparation, Submission, and Execution of the Budget
- OMB Circular A-130, Managing Information as a Strategic Resource
OMB Memoranda
- OMB Memorandum M-15-14, Management and Oversight of Federal Information Technology
- OMB Memorandum M-19-03, Strengthening the Cybersecurity of Federal Agencies by enhancing the High Value Asset Program
- OMB Memorandum M-22-16, Administration Cybersecurity Priorities for the FY 2024 Budget
HHS Policies
- HHS Policy for Information Technology Portfolio Management (PfM)
- HHS Policy for Information Technology Asset Management (ITAM)
- HHS Policy for Records Management
- HHS Policy for Information Security and Privacy Protection (IS2P)
HHS Documents
- HHS System Inventory Management Standard
- HHS EANow User Guide
- HHS SGRC Archer A&A Module User Guide 6.7.24 v9.0
Additional references may be found in Appendix E: References.
6. Policy
It is the policy of HHS that the IT System Inventory that all required data will reside within the EANow tool managed by the HHS EA Program. The overarching requirements and principles for this Policy are detailed in their respective sections below.
6.1. IT System Inventory Requirements
- All HHS entities must identify, register, and maintain a current and accurate inventory of IT systems that are updated as changes occur, or at a minimum, semiannually, throughout the lifecycle as defined in Appendix A.
- All HHS entities must decommission retired IT systems as detailed in Appendix A and in accordance with federal mandates, guidance, and regulations.
6.2. IT System Inventory Principles
- The IT System Inventory must include all IT systems that are owned by, or operated on behalf of, any HHS entity.
- HHS EANow will serve as the system of record for the HHS IT Systems Inventory.
- The IT System Inventory must adhere to federal laws and regulations, and HHS policies, standards, and guidance, as applicable, in Section 5 and Appendix A.
- The IT System Inventory must comply with the HHS Policy for Information Security and Privacy Protection (IS2P) and the requirements as outlined in the HHS System Inventory Management Standard.
- The IT System Inventory must comply with the HHS Policy for Information Technology Asset Management (ITAM) when developing a software-specific inventory.
- The IT System Inventory must comply with the records retention requirements outlined in the HHS Policy for Records Management.
7. Roles and Responsibilities
7.1. HHS Chief Information Officer (CIO)
The HHS CIO, or designee, must:
- Establish, implement, and maintain a current and accurate IT System Inventory that is managed through a change control process, as detailed in Appendix A;
- Ensure all IT systems and related information are maintained in appropriate HHS repositories, as detailed in Appendix A;
- Ensure that all HHS IT systems adhere to federal mandates and regulations, as well as HHS OIS and HHS Privacy and Information Management (PIM) policies and standards;
- Provide a suite of enterprise-level tools to support an effective process of registering, maintaining, and sharing an inventory of IT systems;
- Ensure HHS entities adopt and implement this policy and its associated federal mandates, processes, and guidance, highlighted in Section 5 and Appendix A;
- Ensure inventory compliance with the HHS Policy for Records Management;
- Use IT System Inventory information to comply with various reporting and oversight requirements; and
- Serve as a member of the Information Technology Governance Board (ITGB).
7.2. HHS Chief Enterprise Architect (CEA)
The HHS Chief Enterprise Architect, or designee, must:
- Serve as owner of the IT System Inventory;
- Manage the life cycle of IT systems in the inventory, in coordination with HHS OpDivs and StaffDivs;
- Implement current technologies and methodologies for IT System Inventory data gathering in accordance with relevant federal regulations, as detailed in Section 5. Authorities;
- Collaborate with the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) in sharing applicable inventory information for analytics and to comply with various reporting -requirements;
- Coordinate with the HHS Capital Planning and Investment Control (CPIC) Officer in sharing applicable inventory information for analytics and to comply with various reporting requirements;
- Collaborate with the Vendor Management Office (VMO) in the discovery and sharing of applicable HHS Software Asset Management (SAM) inventory information to comply with various reporting requirements; and
- Coordinate with the HHS Senior Agency Official for Records Management (SAORM) in sharing applicable inventory information for analytics and comply with various reporting requirements.
7.3. HHS Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
The HHS CISO, or designee, must:
- Collaborate with the CEA in the synchronization and sharing of information in the IT System Inventory in EANow and OIS System Inventory in Archer.
7.4. HHS Senior Agency Official for Records Management (SAORM)
HHS CIO also serves as the HHS Senior Agency Official for Records Management. The HHS SAORM must:
- Collaborate with the CEA in the synchronization and sharing of cybersecurity, privacy, and IT System Inventory related information for analytics and to comply with various reporting requirements as detailed in Appendix A.
7.5. HHS IT Capital Planning and Investment Control (CPIC) Officer
The HHS CPIC Officer must:
- Collaborate with the CEA to synchronize and share IT Investment and IT System Inventory information for analytics, ensuring compliance with the reporting requirements outlined in Appendix A.
7.6. HHS Enterprise Architecture Review Board (EARB)
The EARB must:
- Provide expert guidance on IT System Inventory standards, configuration management, and oversight; and
- Provide coordination and validation of the IT System Inventory data.
7.7. HHS Vendor Management Office (VMO)
The VMO must:
- Collaborate with the CEA and CISO in the discovery and sharing of the HHS ITAM Inventory information for analytics and to comply with various reporting requirements as detailed in Appendix A.
7.8. OpDiv CIO
Each OpDiv’s CIO, or designee, must ensure that:
- OpDiv IT System Inventory information is in compliance with this Policy;
- IT System Inventory and OpDiv’s HHS OIS System Inventory are maintained in the appropriate HHS Enterprise repositories; and
- IT System Inventory and OpDiv’s HHS OIS System Inventory adhere to federal mandates and regulations, as well as HHS OIS and HHS Privacy Information Management (PIM) policies and standards, as applicable to the IT System Inventory.
7.9. OpDiv CEA
The OpDiv CEA must:
- Ensure a current and accurate OpDiv IT System Inventory is maintained within the repository, as detailed in Appendix A;
- Collaborate with Business Owners, System Owners, and other functional stewards to ensure the accuracy of the IT System Inventory information;
- Ensure IT system information is maintained throughout the lifecycle in compliance with this Policy and in collaboration with the OpDiv CISO; and
- Coordinate with the HHS SAORM in sharing applicable inventory information for analytics and to comply with various reporting requirements.
7.10. OpDiv CISO
The OpDiv CISO must:
- Ensure IT system information is maintained throughout the lifecycle in compliance with this Policy and in collaboration with the OpDiv CEA; and
- Provide coordination and validation of the IT system data used in the OpDiv HHS OIS System Inventory.
7.11. OpDiv IT Capital Planning and Investment Control (CPIC) Officer
The OpDiv IT CPIC Officer must:
- Ensure IT System Inventory information is maintained throughout the IT system lifecycle in compliance with this Policy and collaboration with the OpDiv CEA;
- Validate and align IT System-to-Investment relationships and ensure it is managed in collaboration with the OpDiv CEA.
7.12. Business Owner
The Business Owner is the executive in charge of the organization who serves as the primary customer and advocate for an IT investment. The Business Owner must:
- Ensure the System Owners are registering and maintaining their IT system(s) to provide a current and accurate IT System Inventory, as detailed in Appendix A.
7.13. System Owner
The System Owner is the technical manager of an IT system and manages the system under the direction of one or more Business Owners. The System Owner must:
- Collaborate within their OpDiv to register, document, and maintain their IT system(s) throughout their lifecycle to provide a current and accurate IT System Inventory, as detailed in Appendix A;
- Provide inventory data to Business Owners to register and maintain their IT system(s) in the IT System Inventory; and
- Share required IT System Inventory information for their IT system(s) with the OpDiv CEA, OpDiv CISO, OpDiv SOP, OpDiv Records Officer, and OpDiv CPIC Officer as specified in Appendix A.
8. Information and Assistance
The HHS Office of Enterprise Architecture is responsible for the development and management of this Policy. Questions, comments, suggestions, and requests for information about this Policy should be directed to HHS_EA_Program@hhs.gov.
9. Effective Date and Implementation
The effective date of this Policy is the date on which the policy is approved. This Policy must be reviewed, at a minimum, every three (3) years from the approval date. The HHS CIO has the authority to grant a one (1) year extension of the Policy. To archive this Policy, approval must be granted, in writing, by the HHS CIO.
10. Approval
/S/
Jennifer Wendel, HHS Chief Information Officer (CIO)
11/22/2024
Appendix A: Procedures
Please note that this appendix is subject to change at any time. The current version of this Policy will always reside in the OCIO Policy Library.
1. IT System Inventory Management Process
The IT System Inventory management process consists of discovery and registration, documentation and maintenance, and decommissioning. A series of activities for each life cycle stage is described in Figure 1.
All OpDivs and StaffDivs are allowed to maintain their inventory management systems.
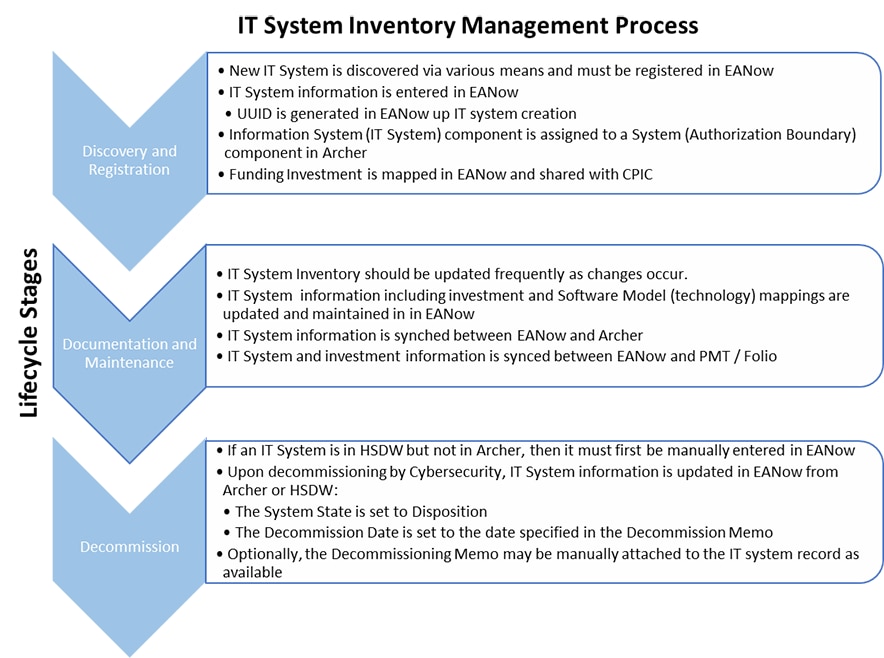
1.1. Discovery and Registration
An IT system is a discrete set of information resources organized for the collection, processing, maintenance, transmission, and dissemination of information. An IT system is funded by one or more investments.
An IT system is uniquely identified by its Universally Unique Identifier (UUID), which is generated upon its creation in EANow. All IT systems must be registered in EANow before getting an ATO.
IT systems may be discovered through various means including, but not limited to, the following: the HHS Enterprise Performance Life Cycle (EPLC), investment reviews, budget requests, acquisitions, expenditures, network scans, cybersecurity audits, and system authorization boundary Authority to Operate (ATO) requests and renewals.
Once an IT system has been registered in EANow, it is shared with both HHS OIS and HHS PIM and is assigned to a system boundary as an information system component in Archer.
1.2 Documentation and Maintenance
As stated in Section 3 of Appendix A EANow serves as the authoritative source for all HHS IT systems. Information in EANow must remain accurate and up to date throughout the lifecycle of an IT system. The information maintained for an IT system includes, but is not limited to, its name, acronym, description, initial operating date, system state, system type, cloud-enabled status, funding investment(s), and associated software/technologies.
From a cybersecurity perspective, information regarding the system boundary and all of its other components are to be documented and maintained in Archer as detailed in the HHS System Inventory Management Standard.
From a CPIC perspective, information regarding the investment is to be documented and maintained in HHS Folio.
1.3 Decommission
When an IT system is ready to be retired, its decommissioning must be coordinated between EA and cybersecurity. In EANow, the decommission date of the IT system must be entered to reflect the date of the decommissioning memo. After the decommission date has been updated, the system state of the IT system must be updated to “Disposition”. Information about a decommissioned system will be retained in EANow for seven (7) years in accordance with guidance from the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA).
From a cybersecurity perspective, information regarding the system boundary and its components needs to be updated to reflect the decommissioning of the IT system in Archer as detailed in the HHS System Inventory Management Standard.
2. IT System Inventory Validation
A semi-annual validation is performed to help ensure that only valid IT systems (including those that have been decommissioned) remain. Confirming that the inventory is both current and accurate, an effective exchange of information between HHS Enterprise Architecture (EA), HHS OIS, and HHS CPIC is possible. Having accurate information across these related data sources makes possible organizational enterprise-wide analysis and data visualization of the Department’s IT assets and supports the Department’s required reporting to the Office of the Inspector General (OIG), Department of Homeland Security (DHS), OMB, and Government Accountability Office (GAO).
For this validation exercise, OpDivs may do their data gathering using whatever means that best suits their environment, if the required data is provided to the HHS EA Program in the appropriate manner.
The following are examples of things that may have been modeled in EANow, but are not valid IT systems, and therefore may be removed from the IT System Inventory:
- Placeholders for IT systems that were modeled, but never became operational.
- IT systems that have been HHS Security Data Warehouse (HSDW) for more than 7 years.
3. Data Requirements
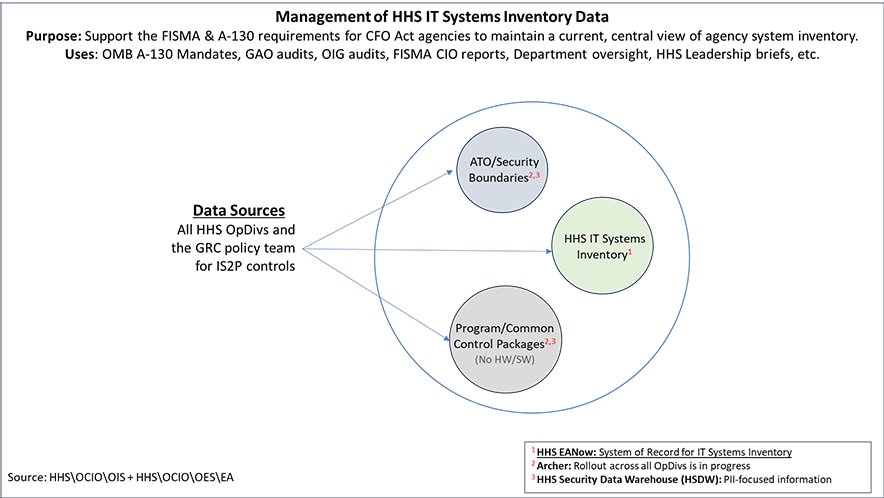
As shown in the diagram above the primary tools involved in the management IT systems inventory data in HHS are:
HHS EANow assigns the required Universal Unique Identifier (UUID) to each HHS IT system upon their registration in the database. This requirement assures that all HHS IT systems are in HHS EANow and makes HHS EANow the system of record for the HHS IT Systems Inventory. This is the focus of this HHS Policy for IT System Inventory Management.
HHS Security Data Warehouse (HSDW) maintains Personally Identifiable Information (PII) related data for each IT system. HHSDW also maintains details on the Program and Common Control Packages associated with each IT system. This data store also maintains on security boundaries and Authority to Operate (ATO) information.
Archer Security, Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (SGRC), widely referred to as Archer is designed to be the primary data store for security-related data for IT systems in HHS. At this point in time, Archer rollout is still in progress across all HHS OpDivs. HSDW will continue to be used even after the Archer rollout is completed.
The information in these data sources is used for addressing GAO audits, OIG audits, FISMA CIO reports, Department oversight, HHS Leadership briefs, and OMB A-130 Mandate for all Chief Financial Officers (CFO) Act agencies to maintain a current, central view of the agency systems inventory (EANow).
As of this Policy publication, the EANow User Guide is being updated to include data requirements for system-level details.
4. Data Sharing
IT systems inventory information is currently shared among HHS EANow, HHS OIS, and HHS CPIC. All necessary data movements are conducted using EANow, HSDW, Archer, and HHS Folio.
As shown in the diagram in Section 3 above, EANow is the authoritative source for all HHS IT systems. HHS EANow, managed by HHS EA, assigns the UUID for all HHS IT systems. As a result, HHS EANow is the system of record for all HHS IT systems. For all data exchanges between IT systems the UUID is used as the primary key.
HHS OIS System Inventory (i.e., IT systems, the system authorization boundaries, common/program control packages), is maintained in HSDW and Archer and is used in the creation of system authorization boundary IDs (SBIDs). IT System Inventory data from EANow is included in the HHS OIS System Inventory through an interface between EANow and Archer.
HHS CPIC is the authoritative source for the IT investment portfolio, which is maintained in HHS Folio. For all data exchanges including investments, the Unique Investment Identifier (UII) is to be used as the primary key.
5. Reporting Requirements
Relevant information about IT systems is maintained in EANow in order to support various HHS, OMB, and GAO reporting requirements as well as for analytics and analysis. These requirements may vary with each cycle.
6. Analytics
Information about all IT systems in EANow will be used to provide meaningful analytics to support IT Budget Reviews, Legacy IT Modernization efforts, technological risk, and alignment to business.
7. Legacy IT Modernization
All IT systems in EANow must specify supporting component software and technologies (e.g., operating systems, databases, middleware, business applications, business intelligence, software development, and productivity) in order to support Legacy IT Modernization analysis and mitigation of IT systems with end-of-life and obsolete software.
Appendix B: Standards
Please note that this appendix is subject to change at any time. The current version of this Policy will always reside in the OCIO Policy Library.
In accordance with federal mandates and regulations and HHS guidance, inventory data must comply with the minimum data standards that will be detailed in the EANow User Guide. The EANow User Guide is being updated for this and other reasons as a separate exercise.
Appendix C: Guidance
Please note that this appendix is subject to change at any time. The current version of this Policy will always reside in the OCIO Policy Library.
1. Relationship between IT System and System
1.1. IT System
An IT system is a discrete set of information resources organized for the collection, processing, maintenance, transmission, and dissemination of information, in accordance with defined procedures, owned or operated on behalf of, and automated to support HHS’s or OpDiv’s mission. An IT system is the codification of business requirements, automated to support a specific mission- or business-related function. An IT system typically encompasses the hardware, software, information, data, applications, communications, and the human resources needed to run the IT system. An IT system is funded by an investment and is composed of technological components such as hardware and software.
The information maintained in EANow for an IT system includes but is not limited to, its name, acronym, description, initial operating date, system state, system type, funding investment(s), and associated software/technologies.
1.2. System
A System is an authorization boundary of which a component may be an IT system (NIST SP 800-57 Part 1, Rev. 5).
A System consists of one or more of the following components to be maintained in Archer as depicted in Figure 3 below:
- Information Systems (system, subsystem, major/minor application, child, or standalone system)3.
- Programs (cybersecurity programs, Privacy programs). Programs can be used for controls operated by groups of people (e.g., cybersecurity programs, Privacy programs). Programs are also inheritance sources4.
- Common Control Providers (CCPs). A Common Control Provider specifies controls for other information systems (components) to inherit.5
2. Naming an IT System
The name created to represent the IT system should be descriptive to reflect the purpose or function the IT System is supporting (e.g., Payroll, Grants, Accounting, etc.) and should be approved by the business owners and/or system owners.
The IT System name will be the official name used for all regulatory and compliance reporting requirements related to, but not limited to Enterprise Architecture (EA), Capital Planning (CPIC), cybersecurity and Privacy, and Records Management throughout its lifecycle.
Although not recommended, the IT System name may be the same as the system authorization boundary name. The system authorization boundary represents aspects extending beyond business systems (security controls, hardware, data exchanges, etc.) as well as the associated business system from EANow.
When developing the name:
- Avoid using an organization name or abbreviation as a prefix or suffix (as the organization may be inferred through the properties and relationships within EANow).
- Avoid using vendor names.
- Avoid special characters.
3. Tools
This section expands on the information provided in Appendix A Section 3 with additional details on the Folio information provided here expands on the details of EANow which is an application on the ServiceNow platform and has an extensive set of data-sharing capabilities and Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). Information is easily exported from the platform to Excel, CSV, XML, JSON, and PDF from any list view.
3.1. EANow
EANow is an application on the ServiceNow platform and has an extensive set of data-sharing capabilities and Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). Information is easily exported from the platform to Excel, CSV, XML, JSON, and PDF from any list view. Representational State Transfer (REST) APIs are available to facilitate more complicated information exchanges.
EANow is maintained by HHS EA and serves as the authoritative source for the IT system inventory.
3.2. HSDW
HHS Security Data Warehouse (HSDW) is an Oracle data warehouse maintained by HHS OIS. HSDW is the authoritative source for the FISMA-related HHS OIS System Inventory and is maintained by the HHS OCIO/OIS Compliance Team. HSDW will continue to be used even after the Archer rollout is complete.
3.3 Archer
Archer is an implementation of the Archer Security, Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (SGRC) platform. Archer is designed to become the authoritative source for the FISMA-related information that HHS OIS needs to meet its requirements. As stated above in Section 3.2, roll out of Archer is still in progress.
3.4. HHS Folio
HHS Folio is an implementation of the GSA Folio platform and is the authoritative source for the HHS investment portfolio. It is maintained by CPIC. Through an interface with EANow, this system provides information on capital investments used to fund the IT systems in EANow.
Appendix D: Forms and Templates
Please note that this appendix is subject to change at any time. The current version of this Policy will always reside in the OCIO Policy Library.
No forms are associated with this Policy.
Appendix E: References
Please note that this appendix is subject to change at any time. The current version of this Policy will always reside in the OCIO Policy Library.
Federal Laws
Clinger-Cohen Act of 1996 (40 U.S.C. Chapter 111 Information Technology Management, General; 40 U.S.C. Chapter 113 Responsibility for Acquisitions of Information Technology)
https://uscode.house.gov/view.xhtml?path=/prelim@title40/subtitle3/chapter111&edition=prelim
https://uscode.house.gov/view.xhtml?path=/prelim@title40/subtitle3/chapter113&edition=prelim
E-Government Act of 2002, Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002
https://uscode.house.gov/view.xhtml?path=/prelim@title44/chapter35&edition=prelim
Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA) of 2014 (44 U.S.C. Chapter 35 Coordination of Federal Information Policy)
https://uscode.house.gov/view.xhtml?path=/prelim@title44/chapter35&edition=prelim
Federal Information Technology Acquisition Reform Act (FITARA) of 2014, FITARA Enhancement Act of 2017 (40 U.S.C. Chapter 113 Responsibility for Acquisitions of Information Technology; 44 U.S.C. Chapter 36 Management and Promotion of Electronic Government Services)
https://uscode.house.gov/view.xhtml?path=/prelim@title40/subtitle3/chapter113&edition=prelim
https://uscode.house.gov/view.xhtml?path=/prelim@title44/chapter36&edition=prelim
Making Electronic Government Accountable by Yielding Tangible Efficiencies (MEGABYTE) Act of 2016
https://www.congress.gov/bill/114th-congress/house-bill/4904
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication (SP) 800-57 Part 1, Revision 5
https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/SpecialPublications/NIST.SP.800-57pt1r5.pdf
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication (SP) 800-59 Part 1, Revision 2
https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/legacy/sp/nistspecialpublication800-59.pdf
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication (SP) 800-37 Revision 2
https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/SpecialPublications/NIST.SP.800-37r2.pdf
Senior Agency Official for Records Management (SAORM) 2023 Annual Report
https://www.archives.gov/files/records-mgmt/agency/nsf-saorm-2023.pdf
National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) Bulletin 2010-02
https://www.archives.gov/records-mgmt/bulletins/2010/2010-02.html
OMB Circulars
OMB Circular A-11, Preparation, Submission, and Execution of the Budget
https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/omb/circulars_a11_current_year_a11_toc
OMB Circular A-130, Managing Information as a Strategic Resource
https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/omb/assets/OMB/circulars/a130/a130revised.pdf
OMB Memoranda
OMB Memorandum M-15-14, Management and Oversight of Federal Information Technology
https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/omb/memoranda/2015/m-15-14.pdf
HHS Policies
HHS Policy for Information Technology Portfolio Management (PfM)
https://www.hhs.gov/web/governance/digital-strategy/it-policy-archive/hhs-policy-information-technology-portfolio-management.html
HHS Policy for Information Technology Asset Management (ITAM)
https://www.hhs.gov/web/governance/digital-strategy/it-policy-archive/hhs-policy-for-information-technology-asset-management-itam.html
HHS Policy for Records Management
https://www.hhs.gov/web/governance/digital-strategy/it-policy-archive/hhs-ocio-policy-for-records-management.html
HHS Policy for Information Security and Privacy Protection (IS2P)
https://www.hhs.gov/about/agencies/asa/ocio/cybersecurity/information-security-privacy-program/index.html
HHS Documents
HHS System Inventory Management Standard
HHS EANow User Guide
HHS SGRC Archer A&A Module User Guide 6.7.24 v9.0
Glossary and Acronyms
Definitions:
Archer – Archer is IT system that serves as the repository for the HHS OIS System Inventory and all FISMA-related information for each system authorization boundary.
Authorization Boundary – All components of an information system to be authorized for operation by an authorizing official. This excludes separately authorized systems to which the information system is connected.
Capital Planning and Investment Control (CPIC) – Is the decision-making process that ensures IT Investments integrate strategic planning, budgeting, procurement, and management with a focus on the missions and business needs of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
Chief Enterprise Architect (CEA) – A senior-level position responsible for leading and overseeing HHS’s or an OpDiv’s Enterprise Architecture (EA) program, practices, and initiatives.
EANow – EANow is the IT system managed by HHS EA that serves as the Department’s authoritative inventory of IT Systems.
Enterprise – An organization supporting a defined business scope and mission. An enterprise is comprised of interdependent resources (people, organizations, and technology) that coordinate functions and share information in support of a common mission (or set of related missions).
Enterprise Architecture - A strategic information asset base that defines the mission; the information and technologies necessary to perform the mission and the transitional processes for implementing new technologies in response to changing mission needs; and includes a current architecture, a future architecture, and a sequencing plan. (Source: The Common Approach to Federal Enterprise Architecture; May 2, 2012).
Enterprise Performance Life Cycle (EPLC) – A methodology that establishes a project management and accountability environment for HHS IT projects to achieve consistently successful outcomes that maximize alignment with Department-wide and individual OpDiv/StaffDiv goals and objectives. Implementation of the EPLC methodology allows HHS to improve the quality of project planning and execution, reducing overall project risk.
Folio – Folio is the HHS CPIC repository for the IT Budget investment portfolio.
HHS Enterprise Architecture Review Board (EARB) – A cross-Division body responsible for guiding the development, implementation, and evolution of the HHS Enterprise Architecture. With its membership from all HHS OpDivs, the HHS EARB aims to ensure consistency, coherence, and efficiency across IT systems and infrastructure within the enterprise. OpDivs and StaffDivs may have an equivalent entity within their domains as well.
HHS EA Program – HHS OCIO EA functions led by the HHS Chief Enterprise Architect.
HHS OIS System Inventory – The inventory of all HHS systems and their related FISMA information as maintained by HHS OIS in HSDW / Archer
HHS Security Data Warehouse (HSDW) – HSDW is the HHS OIS repository for the system inventory (to be replaced by Archer)
Information System – An information system is a component of a System in Archer; See IT System below.
Information Technology (IT) - “IT” is defined as any services, equipment, or interconnected system(s) or subsystem(s) of equipment, that is used in the automatic acquisition, storage, analysis, evaluation, manipulation, management, movement, control, display, switching, interchange, transmission, or reception of data or information by the agency.
IT Investment – ‘Information technology investment’ means an expenditure of information technology resources to address mission delivery and management support. This may include a project or projects for the development, modernization, enhancement, or maintenance of a single information technology asset or group of information technology assets with related functionality, and the subsequent operation of those assets in a production environment.
IT System - An IT system is a discrete set of information resources organized for the collection, processing, maintenance, transmission, and dissemination of information. An IT system is the codification of business requirements, automated to support a specific mission- or business-related function. An IT system typically encompasses the hardware, software, information, data, applications, communications, and people.
IT System Inventory – The inventory of the HHS IT systems that is maintained by HHS Enterprise Architecture in EANow.
Principle – A statement of preferred direction or practice. Principles constitute the rules, constraints, and behaviors that an organization will abide by in its daily activities over a long period of time.
Policy - A policy is a set of principles, rules, and guidelines formulated or adopted by an organization to reach its long-term goals.
System – A system represents an authorization boundary of which all components to be authorized for operation by an authorizing official and excludes separately authorized systems, to which the system is connected.
Acronyms:
- API - Application Programming Interface
- ASA - Assistant Secretary for Administration
- ATO - Authority to Operate
- BO - Business Owner
- BY - Budget Year
- CCA - Clinger-Cohen Act
- CEA - Chief Enterprise Architect
- CIO - Chief Information Officer
- CISO - Chief Information Security Officer
- CPIC - Capital Planning and Investment Control
- CSV - Comma-separated Values
- EA - Enterprise Architecture
- EARB - Enterprise Architecture Review Board
- EPLC - Enterprise Performance Life Cycle
- FEA - Federal Enterprise Architecture
- FISMA - Federal Information Security Modernization Act
- FITARA - Federal Information Technology Acquisition Reform Act
- FY - Fiscal Year
- GRC - Governance, Risk Management and Compliance
- HHS – Department of Health and Human Services
- HSDW – HHS Security Data Warehouse
- HVA – High Value Asset
- IS2P – Information Security and Privacy Protection
- IT – Information Technology
- ITAM – Information Technology Asset Management
- ITGB - Information Technology Governance Board
- JSON – JavaScript Object Notation
- MEGABYTE – Making Electronic Government Accountable by Yielding Tangible Efficiencies
- NARA - National Archives and Records Administration
- NIST – National Institute of Standards and Technology
- OCIO – Office of the Chief Information Officer
- OES – Office of Enterprise Services
- OIS – Office of Information Security
- OMB – Office of Management and Budget
- OpDiv – Operating Division
- PDF – Portable Document Format
- PII – Personally Identifiable Information
- PIM – Privacy and Information Management
- REST – Representational State Transfer
- SAM – Software Asset Management
- SAORM - Senior Agency Official Records Management
- SO – System Owner
- SOP – Senior Official for Privacy
- SP – Special Publication
- StaffDiv – Staff Division
- UII – Unique Investment Identifier
- UUID – Universally Unique Identifier
- VMO – Vendor Management Office
- XML – Extensible Markup Language
Endnotes
1 HHS Security Data Warehouse (HSDW) Escalation Memorandum 2013
2 HHS Inventory Management Standard
3 An Information System component in Archer is the equivalent to an IT system in EANow of which EANow is the authoritative source
4 A Program component in Archer is a cybersecurity concept that is not applicable to an IT System in EANow
5 A Common Control Provider component is a cybersecurity concept. Therefore, it is relevant to the data managed in Archer and is not included in EANow.